How Orion Constellation Can Help You Explore the Cosmos: Sometimes when you look up at night, do the stars take you away? It’s possible to see some of your favorite constellations when you look up at the sky. You may not know this, but constellations are more than what they seem to be. From Earth, constellations tell us stories about the universe. Others are just groups of made-up star patterns. Let’s read about Orion, Orion constellation and orion stars download.
What is a Constellation?
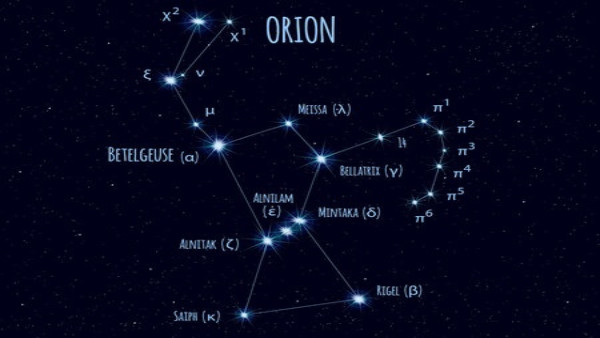
A constellation is a named pattern of stars that resembles a certain shape. Consider it similar to connecting the dots. If you connect the dots – stars in this example – and apply your imagination, the picture will resemble an object, animal, or human. Therefore, the constellation Orion was named after a hunter in Greek mythology. All over the world, you can see this famous formation in the night sky.
During a clear night, the simplest method for locating Orion is to go outdoors and search for three dazzling stars arranged in an almost straight line. These three stars reflect the belt of Orion. Two brighter stars situated to the south symbolize his ankles, while two more illuminate his shoulders in the north.
Throughout history, various cultures across the world have assigned distinct terms and numerical values to constellations, based on their perception of the stars’ resemblance. There are currently 88 officially declared constellations. While a vast majority of these constellations are based on what we can see with our eyes, scientists have created unauthorized constellations for objects visible exclusively in gamma rays, the highest-energy type of light.
Perspective is all that matters
A constellation may appear to be in close proximity from Earth, but they could be separated by a great distance in space. For instance, star Alnitak, which is on the left side of Orion Constellation, is about 800 light-years away. Alnilam, the star in the orion belt’s center, is around 1,300 light-years away. Mintaka, the star on the right side of the belt, is around 900 light-years away.
However, from Earth, they all appear the same brightness. Because space is three-dimensional, you might see an altogether different pattern if you looked at the stars that make up the constellation Orion from another region of our galaxy!
The Orion Superstars
Betelgeuse
Now that we’ve learned a little bit more about constellations, let’s speak about the incredibly interesting celestial bodies that make them up: stars! Though Orion comprises several stars, two stand out. Betelgeuse (Orion’s right shoulder) and Rigel (Orion’s left foot) are the brightest stars in the constellation.
The Sun is about 5 billion years old compared to other stars, while Betelgeuse is only about 10 million years old. What would happen if this star took the place of the Sun at the center of our solar system? It would go through the huge belt of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter! However, because of its size, it has a quick and frantic life.
At the end of Betelgeuse, a supernova explosion will occur. Scientists noticed that Betelgeuse was dimming for no clear reason in late 2019. This was after the star had a very violent explosion that blew off a lot of its visible surface. The Betelgeuse is slowly getting better after what happened, and it doesn’t look like the star is going to explode any time soon, according to Hubble telescope images. Although unlikely, Betelgeuse might go supernova in your lifetime. This event wouldn’t be dangerous for us because Betelgeuse is about 550 light-years away, but it would be amazing to see.
Rigel
Another young star is Rigel, which is thought to be 8 million years old. Rigel is also a star that is much bigger and heavy than our Sun. Despite this, its surface is thousands of degrees hotter than Betelgeuse’s, which is why it shines blue-white instead of red. From Earth, you can see these colors clearly. Not only is Rigel farther away from Earth than Betelgeuse (about 860 light-years), but it is also brighter on its own, making it the biggest star in Orion and one of the brightest in the night sky.
Buckle up for Orion Stars belt
Some of the dots which make up constellations actually include more than one star, although from a considerable distance, they appear to be a single object. Remember Mintaka, the star on the far right side of Orion’s belt? It is not simply one star, but five stars in a complex stellar system. Orion’s Belt is a belt of three stars that runs through the center of the Orion constellation.
Sword or an exceptional nursery?
Situated beneath the three dazzling stars comprising Orion’s belt is his sword, which exposes the renowned Orion Nebula.The nebula is 1,300 light-years away, making it the nearest large star-forming zone to our solar system. Due to its brightness and a prominent spot immediately below Orion’s belt, the Orion Nebula may be seen from Earth. However, the view of the stellar nursery using binoculars may be far more extensive. It appears as a hazy “star” in the midst of Orion’s sword in January.
Distance Between Orion constellation and Earth

The Orion constellation cannot be reached by going to a single spot because it is made up of stars at various positions and distances. The nearest major star (Tabit) in the constellation is 26.32 light-years away, whereas Alnilam is 1,976.75 light-years away. 679.60 light years is the average distance between the main stars. The main stars are the stars that form the outline of a constellation.
Also read: Orion Constellation: A Star Map to the Mysteries of the Universe
Discover more in Orion constellations
Aside from newborn stars, Orion is home to other amazing cosmic objects besides young stars. Exoplanets have been identified orbiting stars outside our solar system. One of them is a huge gas planet three times the size of Jupiter. On average, every star in our galaxy has at least one planet. Think of all the worlds you may glimpse in the night sky!
Because of their distances, we can see how objects looked in the past. To determine how far back we are gazing, multiply the distance by the word “Light” to obtain an indication of how long ago they appeared like that. The object may now appear different.
Furthermore, the Orion Nebula might contain a black hole, making it the nearest known black hole to Earth. Black holes, on the other hand, are hidden since no light can escape them. However, space telescopes equipped with specialized instruments can aid in the discovery of black holes. TIn order to help scientists find clues that will lead them closer to finding some of the universe’s strangest and most interesting things, they may study how matter and stars behave when they are close to black holes.
When you stare at the stars, remember that there is more to them than meets the sight. They may take you to some of the universe’s most magnificent and intriguing objects, such as star systems, young stars, newborn worlds, galaxies, and breathtaking nebulae.





